Abstract
The rapid spread of information in the digital age highlights the critical need for effective fact-checking tools, particularly for languages with limited resources, such as Vietnamese. In response to this challenge, we introduce ViFactCheck, the first publicly available benchmark dataset designed specifically for Vietnamese fact-checking across multiple online news domains. This dataset contains 7,232 human-annotated pairs of claim-evidence combinations sourced from reputable Vietnamese online news, covering 12 diverse topics. It has been subjected to a meticulous annotation process to ensure high quality and reliability, achieving a Fleiss Kappa inter-annotator agreement score of 0.83.
Dataset & Models
Dataset Size
7,232 Claims
Human-annotated pairs
Topics
12 Domains
Multi-domain coverage
Agreement
0.83 Kappa
High reliability
Dataset Creation Process
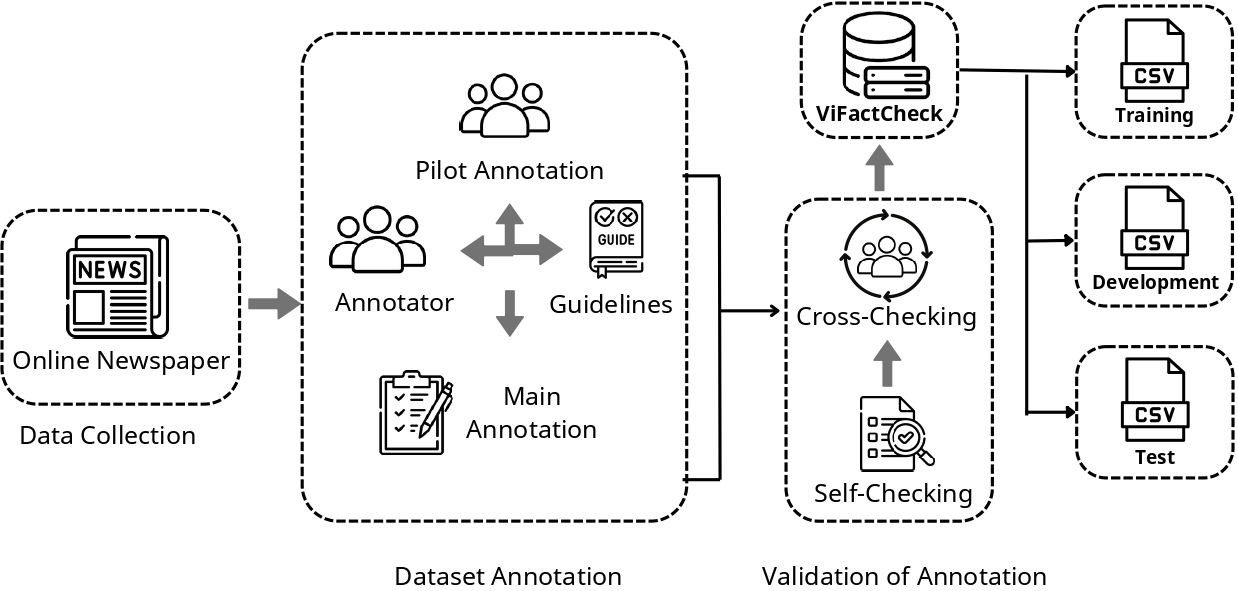
Figure 1: The dataset creation process involves collecting data from reputable Vietnamese news sources, followed by a rigorous annotation process with multiple annotators to ensure high quality and reliability. The process includes data cleaning, annotation guidelines development, and quality control measures.
Available Models
Pre-trained Models
- XLM-R
- ViBERT
- mBERT
- PhoBERT
Large Language Models
-
 Gemma
Gemma
-
 Gemini
Gemini
-
 Mistral
Mistral
-
 Llama
Llama
All models and dataset are publicly available on Hugging Face. You can access them through our Hugging Face Collection.
System Architecture
Our Approach
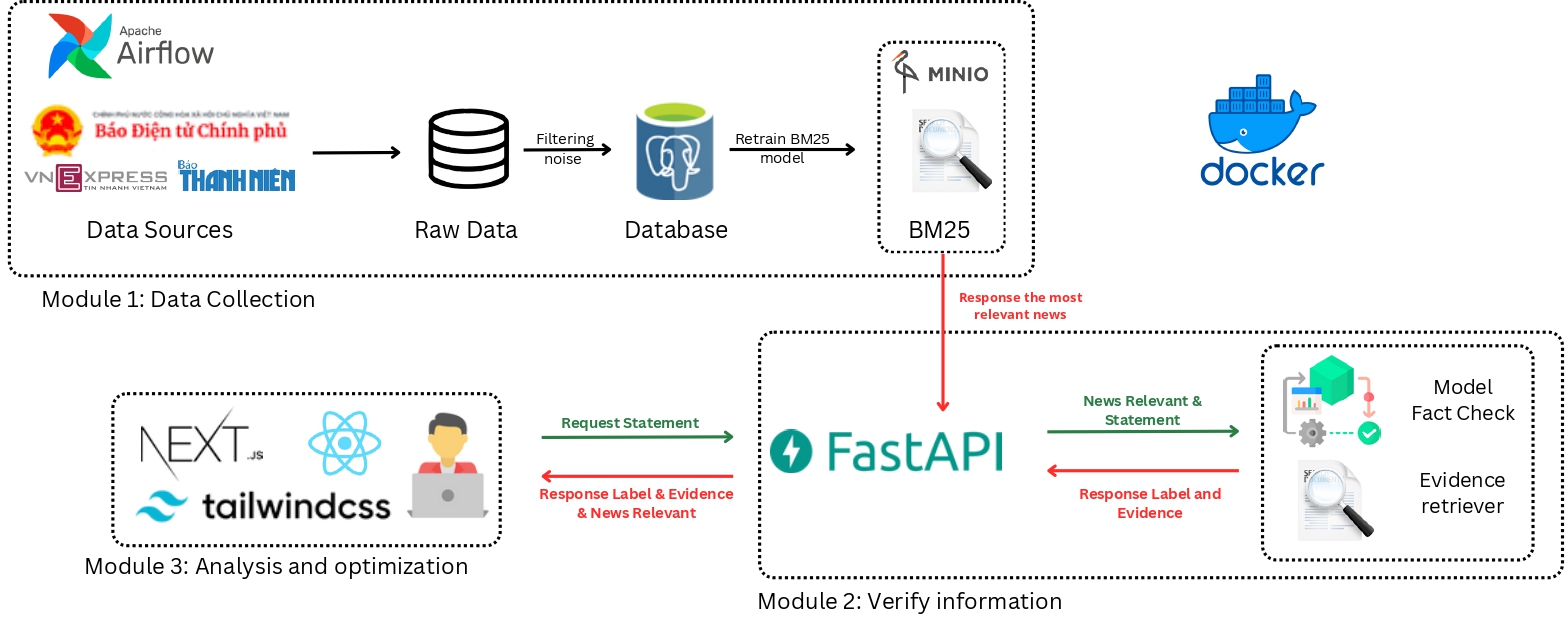
Figure 2: Our system architecture consists of three main components: (1) Evidence Retrieval using SBERT for finding relevant evidence, (2) Multi-evidence Processing to evaluate and combine multiple pieces of evidence, and (3) Fact Verification using fine-tuned language models to determine the veracity of claims.
Results
Leaderboard
| Rank | Team | Model | Full Context | Gold Evidence | Δ | Date |
|---|
Analysis
Model Performance Comparison
Evidence Retrieval Impact
Performance Across Topics
Performance by Text Length
Citation
@inproceedings{hoa2025vifactcheck,
title={ViFactCheck: A New Benchmark Dataset and Methods for Multi-domain News Fact-Checking in Vietnamese},
author={Hoa, Tran Thai and Duy, Tran Quang and Tran, Khanh Quoc and Van Nguyen, Kiet},
booktitle={Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence},
url={https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/32008},
DOI={10.1609/aaai.v39i1.32008},
volume={39},
number={1},
pages={308--316},
year={2025}
}